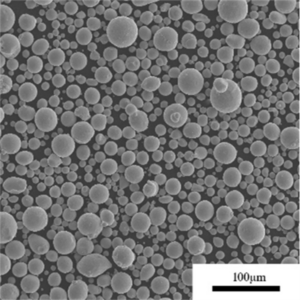
ガス噴霧 is a key process used to produce fine metal powders with precise particle size control. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of gas atomization equipment, including working principles, types, applications, design considerations, suppliers, installation and operation.
How Does Gas Atomization Work?
Gas atomization uses high-velocity gas jets to shatter molten metal into fine droplets that solidify into powder particles. This table summarizes the key principles:
| 動作原理 | 説明 |
|---|---|
| Molten Metal Stream | Molten metal is poured through a nozzle into the atomization chamber |
| High Pressure Gas Jets | Powerful jets of gas (N2, Ar) are ejected from the atomizer |
| Metal Stream Breakup | The gas jets rapidly disintegrate the metal into a spray of fine droplets |
| Rapid Solidification | The droplets quickly solidify into powder particles due to fast cooling |
| パウダーコレクション | The powder particles are collected in vessels below the chamber |
The key advantage of gas atomization is the ability to control particle size distribution by adjusting process parameters. This makes it suitable for producing powders for advanced applications.
Types of Gas Atomizers
There are two main types of gas atomization systems:
Closed-Coupled Atomizers
- Atomization occurs in an enclosed chamber attached directly to the metal pour nozzle
- Allows use of inert/controlled atmosphere
- Limited flexibility in design
Free Fall Atomizers
- Molten metal stream falls freely through atomization chamber
- Provides more flexibility in design
- Open to atmosphere
This table compares the two types:
| パラメータ | Closed-Coupled | Free Fall |
|---|---|---|
| Atmosphere Control | 素晴らしい | 限定 |
| Design Flexibility | Restricted | 高い |
| Gas Consumption | より低い | より高い |
| パウダーの品質 | Superior | 中程度 |
| メンテナンス | Challenging | Relatively Easy |
主要コンポーネント
The major components of a gas atomizer include:
- Melting and pouring unit
- 霧化チャンバー
- High pressure gas supply
- Powder collection system
- Temperature control systems
- Control console

Applications of Gas Atomization
Gas atomized powders find use in many critical applications:
| 産業 | 申し込み |
|---|---|
| 航空宇宙 | Superalloy powders for engines and airframes |
| 自動車 | Powder metallurgy components |
| メディカル | Implant materials like titanium and cobalt alloys |
| エレクトロニクス | Solder and brazing powders |
| アディティブ・マニュファクチャリング | Feedstock powders for 3D printing |
| ハードメタル | Cemented carbide powders |
| Magnets | Rare earth magnet alloys |
The ability to precisely control particle size and morphology makes gas atomized powders ideal for advanced materials production.
Gas Atomizer Design Considerations
Proper design is crucial for achieving desired powder characteristics. Key factors include:
霧化ガス
- Type of gas – inert (Ar, N2) or reactive (O2, N2+H2)
- Gas pressure and flow rate
ノズル設計
- Nozzle diameter, shape, number of nozzles
- Nozzle configuration – annular slit or discrete nozzles
霧化チャンバー
- Shape and size of chamber
- Free fall or closed-coupled design
コレクション・システム
- Collection funnel design
- Separation of fine and coarse powders
- Minimizing oxidation
冷却率
- Gas temperature and pressure
- Distance between nozzle and collection funnel
オートメーション
- Control systems for safe, repeatable operation
- Data monitoring and recording
Proper design is critical for achieving desired characteristics like particle size, shape, and microstructure.
Suppliers of Gas Atomization Systems
There are many equipment manufacturers that design and build gas atomization systems. Here are some of the major suppliers:
| サプライヤー | 所在地 |
|---|---|
| アドバンスト・マテリアル・プロセッシング(AMP) | 米国 |
| 生販在 | 米国 |
| 3D Metal Powder | 米国 |
| Phenix Systems | フランス |
| Superior Shot | カナダ |
| Cyclone Manufacturing | カナダ |
| ISL Vacuum技术 | 中国 |
Buyers need to evaluate suppliers based on:
- Industry experience and reputation
- Track record of successful installations
- Flexibility in design and customization
- After-sales service and support
Prices vary from around $500,000 to over $2 million based on capacity, features and customization.
Installation and Operation
Proper installation and operation procedures are vital for gas atomizers. Here are key considerations:
- Foundations should be designed to handle vibration during operation
- All utilities like power, inert gas, cooling water must be connected appropriately
- Control systems should be calibrated before use
- Initial commissioning should be done with low temperature metals
- Operator training is essential for safety and proper procedures
- Preventive maintenance as per supplier guidelines should be scheduled
Continuous monitoring and analysis of particle size distribution and morphology is needed to ensure desired powder characteristics are achieved.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Routine maintenance is crucial for gas atomizer reliability:
| Task | 頻度 |
|---|---|
| Inspect nozzle and Chamber | 毎日 |
| Check cooling lines | ウィークリー |
| Clean collection system | 毎月 |
| Inspect gas lines for leaks | 毎月 |
| Check control instrumentation | 毎月 |
| Overhaul melt unit | Yearly |
Problems encountered and troubleshooting tips:
| 問題 | Possible Cause | ソリューション |
|---|---|---|
| Irregular powder size | Obstructed/damaged nozzle | Clean or replace nozzle |
| Poor powder yield | Low gas pressure | Check compressor function |
| Oxidized powder | Leak in chamber | Seal leaks and purge with inert gas |
| Powder segregation | Improper collector design | Optimize collection funnel angles |
| Nozzle clogging | Impurities in metal | Use high purity metal, filter melts |
A strict preventive maintenance schedule and monitoring procedures are vital for minimizing downtime. Personnel should be properly trained in troubleshooting techniques.
Choosing a Gas Atomizer Supplier
Here are key considerations for selecting a gas atomizer supplier:
技術的専門知識
- Experience designing atomizers for specific metals or alloys
- Capability to achieve desired particle size and morphology
- Understand requirements like inert operation, protective atmospheres
カスタマイズ
- Flexibility to modify design for production capacity, powder characteristics
- Integration of additional features like degassers, alloying additions
品質
- Consistent powder production meeting specifications
- Reliable equipment with minimum downtime
- Reputation for high-quality manufacturing
サービス
- Technical support for installation, startup, and operation
- Operator training programs
- Availability of spare parts and field service
価格
- Total cost including auxiliary equipment, controls, options
- Cost-benefit analysis of custom features
- After-sales service and maintenance contracts
Prioritizing key requirements and comparing suppliers is important for selecting the right gas atomizer.
Pros and Cons of Gas Atomization
メリット
- Excellent particle size and morphology control
- Applicable to a wide range of alloys
- Inert operation possible to minimize oxidation
- Continuous powder production with good yields
- Automated operation for safety and consistency
制限事項
- High capital and operating costs
- Limited flexibility in alloy changes
- Powders may require secondary processing
- Not suitable for some reactive alloys
- Requires skilled personnel for operation
Gas atomization is the preferred powder production method when precise control over powder characteristics is critical.
Gas Atomization vs Alternative Methods
Comparison with Water Atomization
- Tighter particle size distribution with gas atomization
- Lower oxygen pickup compared to water atomization
- Higher investment cost than water atomization
- Limited alloy range versus water atomization
Comparison with Plasma Atomization
- Finer powder sizes achievable through plasma atomization
- More expensive than gas atomization systems
- Limited production capacity with plasma atomization
- Similar inert atmosphere capabilities
Comparison with Electrode Induction Melting
- Lower productivity than gas atomization
- Limited ability to control particle size and shape
- Simple and low cost process compared to gas atomization
- Only suitable for easily melted metals
Gas atomization provides the best balance of particle size control and reasonable productivity for many critical powder metallurgy applications.
Future Outlook for Gas Atomization Technology
The future prospects for gas atomization look positive due to several trends:
- Increasing use of additive manufacturing drives demand for fine powders
- Need for customized powder characteristics for advanced materials
- Development of novel gas atomization nozzle designs
- Expansion into wider range of alloys including metal oxides
- Automation and IoT integration for better process monitoring
- Use of gas atomization for micro-structured particles
- Adoption of gas atomization in developing countries
Gas atomization equipment will continue evolving to meet the powder requirements of emerging technologies and advanced materials.

よくあるご質問
Q: What is the smallest particle size that can be achieved with gas atomization?
A: Gas atomizers can achieve powders down to around 5 microns by optimizing parameters like gas pressure, nozzle design, and collection distance. However, the production rate significantly decreases at very fine sizes.
Q: How much monitoring and control is required when operating a gas atomizer?
A: Continuous monitoring of temperature, gas pressure, and powder size distribution is necessary. Automated Programmable Logic Controls are typically used to monitor and regulate all process parameters.
Q: What maintenance needs to be done on gas atomization equipment?
A: Nozzles, gas lines, and filters need regular inspection and replacement if obstructed. Water cooling lines need to be checked. The melt unit requires yearly overhauls. Proper maintenance minimizes downtime.
Q: How quickly can gas atomizers be switched between different alloys?
A: Alloy changeover takes 1-2 days depending on the material sequence. Nozzles and lines need to be cleared out to avoid cross-contamination between alloy powders.
Q: What safety measures are required for gas atomization?
A: Proper personnel protective equipment, gas monitors, emergency shut-offs, and training on safety procedures are mandatory. Inert gas operation also improves safety.
Q: What is the typical production capacity of industrial gas atomizers?
A: Production capacity ranges from 50 kg/hr for benchtop lab-scale units to over 1000 kg/hr for high-capacity industrial gas atomizers, depending on the design and nozzle size.
Q: What expertise is needed to properly operate gas atomization equipment?
A: Personnel need training in areas like melt pouring, powder processing, instrumentation, mechanical systems, and troubleshooting. Metallurgical knowledge is also very advantageous.