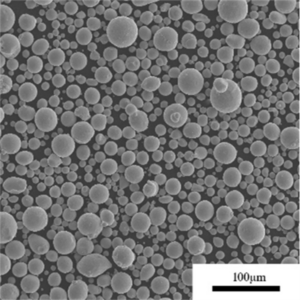
Metal atomisation is a process where metal is converted from its bulk form into fine powdered metal through atomisation. It is commonly used in the production of metal powders for various applications across different industries. This article provides a comprehensive guide on metal atomisation covering the key aspects in detail.
Overview of Metal Atomisation
Metal atomisation involves breaking up molten metal into fine droplets using a high velocity gas or liquid stream. As the droplets solidify rapidly in flight, fine spherical metal powders are formed.
主な詳細
- Used to produce fine spherical metal powders from metals like aluminum, copper, iron, nickel etc.
- Classified into gas atomisation, water atomisation and centrifugal atomisation based on method
- Powders range from 10 microns to 250 microns in size with tight distribution
- Achieves rapid solidification of droplets resulting in fine grained powders
- Mainly used in metal powder metallurgy and for manufacture of metal powder components
Atomisation Methods
| 方法 | 詳細 |
|---|---|
| Gas Atomisation | Molten metal stream disintegrated by high pressure inert gas jets |
| Water Atomisation | Uses water jets for disintegration of metal stream |
| Centrifugal Atomisation | Molten metal poured on spinning disc and flung off edges |
金属粉末の用途
| 申し込み | 詳細 |
|---|---|
| 粉末冶金 | Press and sinter powder compacts to manufacture PM parts |
| 金属積層造形 | Use atomised powders as feedstock for AM processes like DED, PBF |
| Metal Injection Moulding | Mix powders with binder, inject into moulds and debind/sinter |
| 溶射コーティング | Spray atomised powders onto surfaces using plasma/combustion spray |
| ろう付け | Use atomised powder interlayers for high temperature brazing process |
| 溶接 | Atomised metal powders used as filler material in welding processes |
Metal Atomisation Specifications
| パラメータ | 典型的な範囲 |
|---|---|
| パウダーサイズ | 10 to 250 microns |
| サイズ分布 | Tight, spherical morphology |
| 純度 | 最大99.9% |
| 見かけ密度 | Around 40-50% of true density |
| 酸化物含有量 | <1%, lower in inert gas atomisation |
| 生産率 | 10 – 100 kg/hour |

Metal Atomisation Equipment
The key equipment involved in the metal atomisation process includes:
Metal Atomisation Equipment Guide
| 設備 | 目的 |
|---|---|
| Induction furnace | Melts metal charge material into liquid state |
| Crucible | Holds molten metal before pouring into atomiser |
| タンディッシュ | Acts as reservoir facilitating pouring of metal |
| Atomisation mechanism | Disintegrates molten metal into droplets using gas/liquid jet |
| Powder collection system | Collects & separates atomised powder from transport gas/liquid |
Atomiser Types and Characteristics
| Atomiser | 原則 | Features |
|---|---|---|
| Gas Atomiser | High pressure inert gas jet | Finer powder, lower oxidation |
| Water Atomiser | High velocity water jet | Higher production rate, larger particles |
| Centrifugal Atomiser | Molten metal poured on spinning disc/cup | Compact, easy to operate |
Auxiliary Equipment
- Metal charge materials, gases, water
- Pumps, valves, nozzles
- Temperature control and monitoring
- Control panel, instrumentation
- Sieving station for classification
- Dust extraction and gas cleaning systems
Design Standards and Installation Requirements
- Built to standards like ASTM B213 for gas atomisation
- Custom engineered to meet production requirements
- Requires inert gas supply, water supply, electricals
- Installation area depends on atomiser footprint
- Dust extraction, waste water management necessitated
Metal Atomiser Suppliers
主要サプライヤー
| サプライヤー | 所在地 | 製品紹介 |
|---|---|---|
| 生販在 | カナダ | Gas, water and centrifugal atomisers |
| ALD真空技術 | ドイツ | Gas and water atomisers |
| Sino Steel Thermo | 中国 | Water and gas atomisers |
| VTI Vacuum Technologies | 英国 | High-end gas atomisers |
価格
- Small laboratory units start around $100,000
- Industrial scale production atomisers range from $500,000 to $2,000,000
- Larger bespoke systems can cost up to $4,000,000
- Additional costs for auxiliaries, installation, consumables
Choosing Atomiser Supplier
- Reputation and experience level
- Customisation and size range capabilities
- 生産能力とリードタイム
- 予算の制約
- Location and service support
- Powder specification requirements
- Auxiliary equipment offerings
Metal Atomiser Operation
Typical Atomisation Process
| ステップ | アクティビティ |
|---|---|
| 1 | Charge induction furnace with metal to be atomised |
| 2 | Melt metal completely and allow to reach superheat temperature |
| 3 | Start inert gas flow in atomiser at desired pressure |
| 4 | Open induction furnace and pour molten metal into tundish/crucible |
| 5 | Allow metal to flow into atomiser for disintegration into powder |
| 6 | Powder carried by gas into cyclone separators for collection |
| 7 | Sieve powder to remove large particles and fines |
| 8 | Pack final powder into containers after cooling |
Critical Process Parameters
- Superheat temperature of metal
- Molten metal flow rate into atomiser
- Gas/water flow rate and pressure
- Pouring configuration andmetal charge quantity
- Nozzle design and geometry
- Collection and sieving approach
Maintenance Aspects
- Inspect and replace worn out nozzles, valves, liners periodically
- Check gas lines, water jets for blockages affecting flow
- Monitor drive and bearings of centrifugal atomiser
- Clean powder deposition inside pipes and vessels
- Maintain induction furnace, temperature sensors etc.

利点と限界
Benefits and Advantages
- Produces fine, spherical powders ideal for AM, MIM etc.
- Achieves high powder production rates
- Consistent and tight particle size distribution
- Good purity from inert gas atomisation
- Flexible size range from 10 μm to 300 μm
- Scalable process capable of tonnage production
Disadvantages and Limitations
- Water atomised powder can be highly oxidised
- Centrifugal atomiser has size limitation
- Particle size distribution control can be difficult
- Very fine powder poses safety issues
- High capital investment for equipment
- Process requires stringent controls and optimisation
How to Choose a Metal Atomiser
選択のための主な考慮事項
- Type of metal to be atomised
- Desired powder quantity, size and shape specs
- Purity levels and oxygen content required
- Budget constraints and expansion plans
- Available floor space and height
- Auxiliary systems capability
- Level of automation and control needed
- After sales service and maintenance
- Compliance to standards and certifications
Making the Right Choice
- Shortlist suppliers based on experience, capability and reviews
- Specify powder requirements and get design proposals
- Compare options on cost, production rate, features
- Evaluate auxiliary equipment quality, warranty
- Check supplier production and delivery timelines
- Validate design, installation and after sales support
- Choose modular, customisable atomiser for flexibility
- Prioritise quality and tight distribution over lowest cost
- Select supplier willing to co-develop systems for specific needs

よくあるご質問
Q: What is the typical size range of atomised metal powder?
A: The particle size range for most atomisers is around 10 microns to 250 microns. Gas atomisers can achieve finer powder down to 10 microns while water atomisers make coarser powder over 100 microns.
Q: What metals can be atomised into powder form?
A: Common metals atomised include aluminum, copper, iron, nickel, cobalt, titanium, tantalum, stainless steel. Even alloys and reactive metals like magnesium can be atomised.
Q: How spherical are the atomised powders?
A: Atomised powders have highly spherical morphology because the droplets solidify rapidly in flight. Sphericity levels of 0.9 to 1 are achieved. Gas atomisation makes more spherical powder.
Q: What is the main use of atomised metal powder?
A: The primary use is in powder metallurgy for pressing and sintering components. The fine powders are also ideal for metal additive manufacturing using powder bed fusion or directed energy deposition.
Q: How is powder size distribution controlled in atomisation?
A: Nozzle design, molten metal flow rate, gas pressure and atomising configuration determines particle size distribution. Multiple sieving stages post atomisation help narrow the distribution.
Q: Does metal atomisation require special skills?
A: While it is an automated process, skills in areas like metallurgy, thermal spraying, powder handling are needed to optimise and control the atomiser properly for quality metal powder production.
Q: What dictates the production rate of an atomiser?
A: The metal flow rate, gas pressure and atomiser capacity determines production rate. Industrial atomisers can make 100 kg/hr of powder while lab atomisers may make only a few kg/hr.
Q: How to determine the right atomiser size and type?
A: Key factors are powder quantity required, budget, existing infrastructure support and desired powder characteristics. These help shortlist between gas, water or centrifugal type in the needed capacity.
Q: Does metal atomisation produce any waste by-products?
A: Not much solid waste, but effluent gas/water treatment is needed. Dust extraction from powder handling areas is also required. Proper disposal of used filters and consumables is required.
結論
Metal atomisation allows converting bulk metal into fine spherical powders using gas, water or centrifugal energy. With tight control of process parameters, high purity, customised powders ideal for AM can be produced. This guide has summarised the working, types, applications, suppliers and technical considerations for metal atomisation systems. The structured information allows easy comparison between options to choose an appropriate atomiser.