Metal powders are widely used across additive manufacturing, metal injection molding and other powder metallurgy applications. This article provides an overview of various metal powders, production methods, properties, specifications, applications, pricing, 金属粉サプライヤー as well as advantages and limitations of powder-based technologies.
概要 of metal powders
Metal powders processed into end-use components offer benefits like:
- Customized alloys/compositions unattainable via ingot metallurgy
- Intricate, lightweight geometries through additive manufacturing
- Net shape fabrication reducing wastage versus subtractive methods
- Isotropic properties from rapid solidification versus casting
Common metal powders range from stainless steels, tool steels, superalloys to titanium, aluminum, copper and exotic alloys. Production via inert gas atomization, water atomization and plasma rotating electrode process allow tailoring particle size distribution, morphology and microstructure for different applications.

金属粉末の種類
ステンレス鋼
Austenitic and martensitic stainless steel powders like 316L, 420, and 17-4PH offer good corrosion resistance and high hardness after heat treatment:
| グレード | プロパティ | アプリケーション |
|---|---|---|
| 316L | Excellent corrosion resistance, great weldability/formability | Pumps, valves, marine hardware |
| 420 | 高硬度、耐摩耗性 | Cutting tools, bearings |
| 17-4PH | High strength, moderate corrosion resistance, good toughness after aging | Aerospace and industrial components |
工具鋼
Air-hardening tool steels like H13 and D2 provide very high hardness levels after heat treatment:
| グレード | Hardness Range | 用途 |
|---|---|---|
| H13 | 50-55 HRC | Injection molds, dies, tooling |
| P20 | 30-40 HRC | プラスチック射出成形金型 |
| D2 | 60-62HRC | Cutting tools, forming dies |
超合金
Nickel, iron and cobalt-based alloys offer exceptional high temperature strength for extreme environments:
| グレード | Max Service Temp | 用途 |
|---|---|---|
| インコネル718 | 700°C | Aerospace components and systems |
| インコネル625 | 980°C | Aerospace turbines, petrochemical equipment |
| ヘインズ 282 | 870°C | Jet engine parts, land-based turbines |
| コバルト・クローム | 500°C | 医療用/歯科用インプラント |
Aluminum & Titanium
Light metals like aluminum and titanium alloys enable lightweight structrual parts combined with good corrosion resistance (Ti) and high strength-to-weight ratio:
| グレード | 用途 |
|---|---|
| AlSi10Mg | Aerospace and automotive components, prototypes |
| Ti-6Al-4V | Aerospace structural parts, biomedical implants |
Copper & Tungsten
Copper offers high thermal and electrical conductivity while tungsten grades provide extreme hardness and density up to 18 g/cc:
| 素材 | アプリケーション |
|---|---|
| 銅 | Heat sinks, electrodes, welding tips |
| タングステン重合金 | Radiation shielding, vibration damping |
Exotic Alloys
Advanced grades include precious metals, refractory metals and rare earth permanent magnets:
| グレード | 構成 | 用途 |
|---|---|---|
| Elgiloy | Co-Cr-Ni + trace elements | Medical devices, fasteners |
| Nitinol | ニッケルチタン | Actuators, cryogenic apps |
| Neodymium magnets | Nd-Fe-B | Motors, generators, sensors |
These enable specialized electrical, magnetic, thermomechanical and biocompatible properties for niche applications.
生産方法
Gas atomization is the primary technique for fabricating defined particle size distributions optimized for additive manufacturing, metal injection molding etc. Water atomization serves cost-driven applications like powder injection molding bushings and filters.
ガス噴霧
High pressure inert gas (usually argon or nitrogen) sheers off fine molten metal droplets from the melt stream which rapidly solidify into spherical powders ideal for layer-by-layer fusion. Desired chemistry and microstructure are built into the alloy before atomization. This facilitates high powder purity and consistent composition tailored to part functionality.
水の霧化
In this process, molten metal stream is disintegrated by high velocity water jets into fine particles which cool rapidly to form irregular shapes. It is a cheaper process useful for high volume applications where loose powder characteristics are acceptable.
回転電極プロセス
In this method, an electric arc melts a rotating bar feeding into a plasma torch. The evaporated metal condenses in an inert gas atmosphere and the spinning molten particles form spherical powder. It offers extremely fine control over particle size distribution for niche applications.
Properties and Specifications
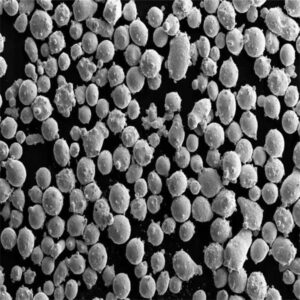
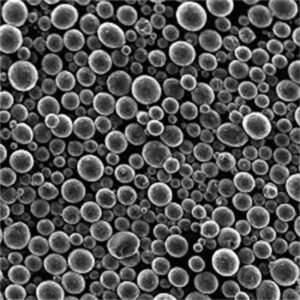
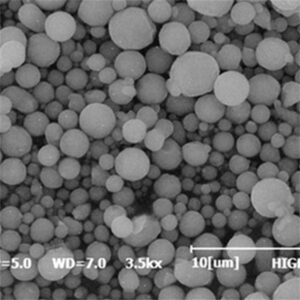
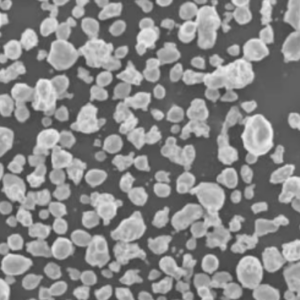
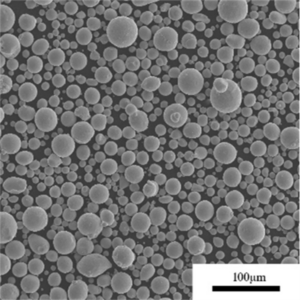
Key powder characteristics like particle shape, size distribution, flow rate and apparent density govern performance in downstream processes like additive manufacturing:
| パラメータ | 典型的な範囲 | 意義 |
|---|---|---|
| 粒子形状 | 球状が好ましい | Influences packing density, flowability, spreadability during printing |
| サイズ分布 | 15-45 μm(代表値 | Impacts min feature resolution, surface finish, density |
| 流量 | 25-40 s/50g | Indicates powder fluidization, spreadability, reduced agglomeration |
| 見かけ密度 | Up to 65% of theoretical | Needed for high densification during sintering or melting |
| 残留炭素 | < 0.01% | Determines oxygen/nitrogen pickup affecting mechanicals |
Material test reports from reputed metal powder suppliers showcase detailed characterization data to choose the right grade for intended application and process.
Application Areas
アディティブ・マニュファクチャリング
- Aerospace components – blades, impellers, engine sections
- Medical implants – orthopedic/dental, surgical tools
- Automotive – valves, pistons, manifold
- Industrial tooling – cutting tools, dies, molds
金属射出成形
- Small precision parts – gears, nozzles, fasteners
- Orthopedic screws, knee/hip implants
- Automotive mechanisms – locks, pulleys
溶射コーティング
- Wear resistant layers – pump shafts, rollers
- Corrosion protection – valves, pipes, vessels
Powder Press and Sinter
- Self-lubricating bearings
- Permanent magnets
- Structural parts via cold/hot isostatic pressing
Tailored powder characteristics enable diverse applications leveraging net shape or near-net shape fabrication.
金属粉サプライヤー
Leading European, Asian and North American suppliers cater to metal powder demand across industries and geographies.
| 会社概要 | 材料 | 定員 | Markets |
|---|---|---|---|
| サンドビック | Stainless, tool steels, superalloys | 210,000 MT | ヨーロッパ、アジア |
| GKN | Stainless steels, superalloys, Ti alloys | 170,000 MT | Europe, North America |
| プラクセア | Ti, Ni, Co alloys | 110,000 MT | North/South America |
| ホーガナス | Tool steels, stainless, low alloy steels | 100,000 MT | ヨーロッパ、アジア |
| リオ・ティント・メタル・パウダーズ | Aluminum, Ti, intermetallic grades | 75,000 MT | Global |
These companies offer wide capability in atomization processes matched by rigorous in-house quality control on powder characteristics and cleanliness backed by certified test reports on chemistry, particle size distribution, microstructure and batch consistency.
Application experts help customize existing alloys or engineer new grades tailored to customer mechanical property, geometry and functionality needs from prototyping to commercial scale metal powder orders.
Metal Powder Pricing
| 素材 | 価格帯 |
|---|---|
| ステンレス 316L | $5-20/kg |
| Maraging steel | $30-60/kg |
| Tool steel H13 | $12-30/kg |
| インコネル718 | $50-150/kg |
| チタン Ti-6Al-4V | $100-500/kg |
Prices depend significantly on order volume, quality grade (commercial, aircraft, medical etc.), regional demand dynamics and extent of certification. Large OEM approved customers get much lower pricing of even $30-40/kg for common aerospace superalloys.
Pros and Cons of Powder Metallurgy
メリット
- Custom alloys/compositions outside conventional ingot metallurgy range
- Complex geometries from additive manufacturing with reduced assembly
- Near net shape fabrication with lower raw material wastage
- Enhanced mechanical properties from rapid solidification
制限事項
- Generally slower production rates than casting or forging
- Additional steps like CIP/HIP needed in AM to improve density
- Reuse of powder can result in changed characteristics
- Requires handling systems to recover/recycle unused powder

概要
In summary, key metal powder types span stainless, tool and superalloys plus aluminum/titanium used across additive manufacturing, metal injection molding and thermal spray coatings. Gas, water and plasma atomization enable tailored powder size distribution, shape and microstructure. Leading global suppliers certified quality matched to application requirements in terms of chemistry, particle characteristics and cleanliness. For prototyping or volume production, matching the proper metal powder type to functionality, process and part performance needs drives overall fabrication success.
よくあるご質問
金属粉はどのようにして作られるのか?
Most commercial powders rely on inert gas atomization or water atomization processes to generate fine spherical particles with tightly controlled size distribution.
What are the main types of metal powders?
Common classifications include stainless steels, tool steels, superalloys, aluminum/titanium alloys, tungsten heavy alloys and precious metals including exotics like Elgiloy, Nitinol etc.
What factors affect metal powder pricing?
Prices depend significantly on volume, extent of certification, regional demand dynamics, raw material costs and alloy composition – exotic superalloys can cost 5-10X stainless steel grades per kilogram.
What are typical sizes for metal powders?
A standard distribution for additive manufacturing lies between 15-45 microns. Water atomized grades can range from 45-150 μm used mainly for pressing and sintering.
What governs choice of metal powders?
Key considerations are part functionality (operating temperature, stresses etc.), fabrication method (casting, MIM, AM), cost targets, extent of post processing and availability in desired product form.
How are metal powders characterized and specified?
Typical parameters provided in material test reports cover powder composition, particle size distribution, morphology (spherical/irregular), flow characteristics, apparent density and residual impurity levels. These govern fitness for service.
Are there standards for metal powders?
ASTM, ASME, MPIF, ISO and equivalent national/regional standards help define specifications for common grades in terms of chemistry, manufacture, sampling procedures, testing methodology, supply condition and quality assurance.
What precautions are necessary when handling metal powders?
Key risks involve flammability and explosion hazards. Inert gas glove boxes, enclosed conveyor/transport systems, grounding, antistatic coatings help safe powder handling alongwith personal protective gear use during extraction and transfer.