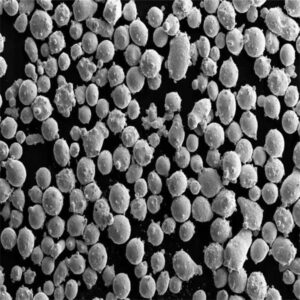
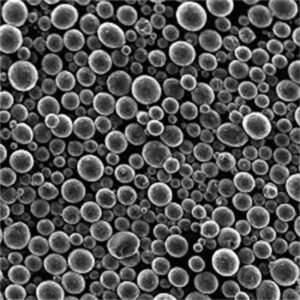
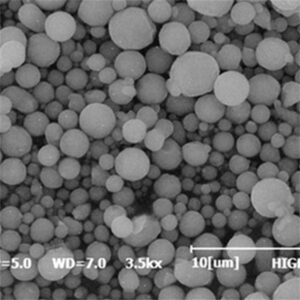
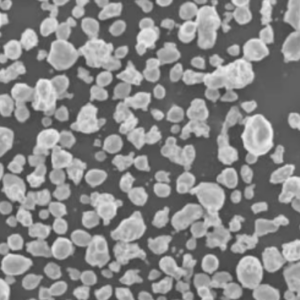
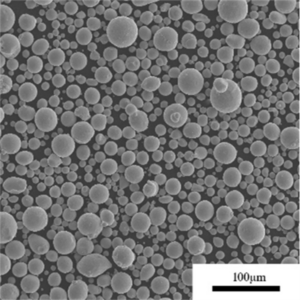
概要 ニオブ合金粉末
Niobium alloys powder refers to powder metallurgy forms of niobium-based alloys. Niobium, also known as columbium, is a refractory transition metal with symbol Nb and atomic number 41. It has a high melting point, good strength at high temperatures, and resistance to corrosion.
Niobium alloys leverage these desirable properties of niobium for applications requiring heat resistance like jet engines, rockets, gas turbines, nuclear reactors, and heat exchangers. The addition of alloying elements creates niobium alloys with enhanced high temperature strength, creep resistance, oxidation resistance etc. compared to pure niobium.
Some commonly used niobium alloys include Nb-Ti, Nb-Zr, Nb-Mo, and Nb-Hf alloys. The alloy powder can be compacted into bespoke component shapes using powder metallurgy techniques. This allows complex geometries to be formed near net shape, minimizing material waste. The methods used include pressing and sintering, metal injection molding, hot isostatic pressing, and additive manufacturing.
The global niobium alloys powder market was estimated at $xx million in 20xx and is projected to reach $xx million by 20xx, growing at a CAGR of xx% during the forecast period. The major drivers are increasing use in aerospace engines, growing adoption in oil & gas industry, and expanding usage in medical devices.

Types of Niobium Alloys Powder
| 合金 | エレメント | 主要物件 | 一般的な用途 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Niobium-Titanium (Nb-Ti) | Niobium + Titanium | Corrosion resistance, strength at low and high temperatures | Nuclear reactors, heat exchangers, superconducting magnets |
| Niobium-Molybdenum (Nb-Mo) | Niobium + Molybdenum | High temperature strength, creep resistance | Aircraft engines, rocket sub-assemblies |
| Niobium-Zirconium (Nb-Zr) | Niobium + Zirconium | Good oxidation resistance, reasonable ductility | Industrial heating elements, glass processing equipment |
| Niobium-Hafnium (Nb-Hf) | Niobium + Hafnium | 優れた高温特性 | Rocket nozzles, turbine blades, nuclear fuel cladding |
Properties of Niobium Alloys Powder
| プロパティ | 説明 |
|---|---|
| 高強度 | Has 0.2% yield strength > 100,000 psi from cryogenic to moderately elevated temperatures |
| 耐熱性 | Retains strength and resist deformation at temperatures exceeding 1000°C |
| 耐酸化性 | Forms protective oxide layer to resist oxidation in air up to 700°C |
| 耐クリープ性 | Resists deformation under load at high temperatures |
| 耐食性 | Withstands many organic and inorganic chemicals, acids, alkalis etc. |
| Easy fabrication | Can be forged, rolled, drawn into wire, welded by conventional methods |
| Non-toxic | Considered non-hazardous, safe for medical and food contact uses |
Characteristics of Niobium Alloys Powder
| 特徴 | 典型的な範囲 |
|---|---|
| 粒子形状 | Spherical, irregular rounded |
| 粒子径 | 1~150ミクロン |
| 見かけ密度 | 2 – 6 g/cc |
| タップ密度 | 4 - 8 g/cc |
| 純度 | >= 99% niobium by weight |
| 酸素含有量 | < 2000ppm未満 |
| 水素含有量 | < 50 ppm |
の応用 ニオブ合金粉末
| 産業 | アプリケーション |
|---|---|
| 航空宇宙 | Jet engine components, rocket subassemblies, missile bodies |
| エネルギー | Oil drilling equipment, nuclear fuel cladding, solar panel frames |
| 自動車 | Turbocharger parts, fuel injection systems |
| メディカル | MRI machines, pacemakers, surgical tools |
| ケミカル | Heat exchangers, corrosion-resistant vessels |
仕様と規格
Niobium alloys powder is available in various specifications targeting the requirements of different applications:
| スタンダード | 組織 | 詳細 |
|---|---|---|
| AMS5815 | SAE Aerospace | Chemical compositions for wrought niobium alloys |
| ASTM B393 | ASTM | Standard specification for niobium metal, bar, billet, wire |
| ISO 15371 | 国際標準化機構 | Chemical, mechanical, fabrication properties |
| MIL-STD-2207 | US Military | Protective treatments, quality assurance testing |
The powder can be certified to conform to ISO 9001 quality management and ISO 14001 environmental standards.
サプライヤーと価格
Some leading global suppliers of niobium alloy powders include:
| サプライヤー | Brands | 価格 |
|---|---|---|
| CBMM | CBMM C-103, CBMM C-129Y | $xx to $xx per kg |
| Stanford Materials | SN-1, SN-2, SN-3 | $xx to $xx per kg |
| エッジテック工業 | EBM Niobium 702, 718, 720 | $xx to $xx per kg |
| 特殊金属 | IN-100, IN-713, IN-725 | $xx to $xx per kg |
Pricing can range widely depending on alloy composition, particle size distribution, lot quantity, and purchase terms.
の長所と短所 ニオブ合金粉末
| 長所 | 短所 |
|---|---|
| Excellent strength at high temperatures | 比較的高価 |
| Good fabricability into components | Limited commercial availability |
| Resists oxidation and corrosion | Prone to embrittlement from contamination |
| Bio-compatible for medical uses | Oxide layer makes welding difficult |
| Custom alloys can be developed | 管理された雰囲気での処理が必要 |
よくあるご質問
Q: What is niobium alloy powder used for?
A: Niobium alloy powder is used to manufacture high performance parts for aerospace, energy, automotive, medical, and chemical industry applications requiring good heat resistance, strength at high temperatures up to 1000°C, resistance to oxidation and corrosion etc.
Q: How is niobium alloy powder made?
A: It is produced by gas atomization process where a stream of molten niobium alloy mixture is disintegrated by jets of argon or nitrogen gas into fine droplets that solidify into powder particles in the micron size range. The powder can also be made via rotating electrode process or plasma rotating electrode process.
Q: What technologies are used to process niobium alloy powder?
A: Key powder processing routes are pressing and sintering, metal injection molding, hot isostatic pressing, and additive manufacturing methods like laser powder bed fusion, binder jetting, and directed energy deposition. These techniques can fabricate complex and near-net shaped niobium parts.
Q: What are the essential elements that are alloyed with niobium?
A: The most common alloy additions are titanium, molybdenum, zirconium, hafnium, tungsten, tantalum etc. These elements enhance properties like strength, creep resistance, oxidation resistance, and workability of niobium-based alloys. The optimum composition depends on the application.
Q: What standards does niobium alloy powder conform to?
A: Key standards include SAE AMS 5815 covering niobium alloy chemistry limits; ASTM B393 for niobium metal specifications; ISO 15371 defining mechanical, physical and fabricability properties; MIL-STD-2207 on protective treatments and quality testing; and international standards for quality management (ISO 9001) and environmental responsibility (ISO 14001).