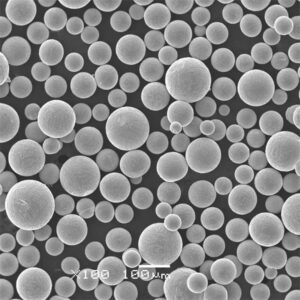
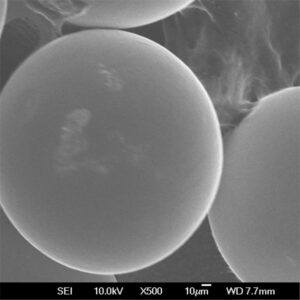
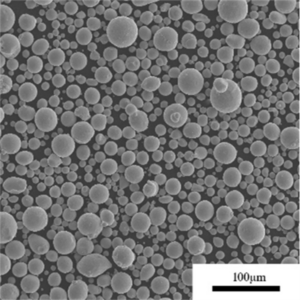
チタンパウダー is a versatile metal powder with unique properties that make it an important material for many applications. This article provides an overview of titanium powder, its properties, production methods, applications, and leading global suppliers.
Overview of Titanium Powder
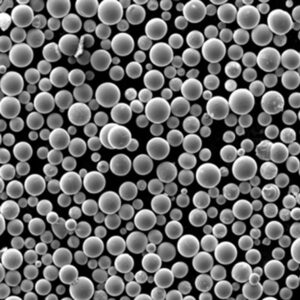
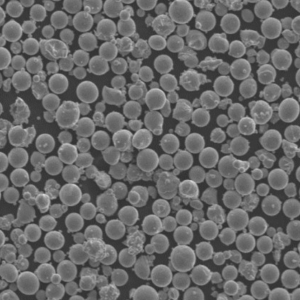
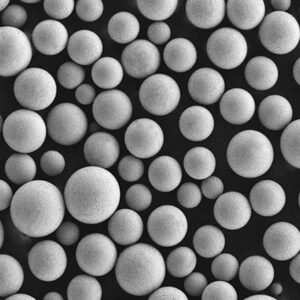
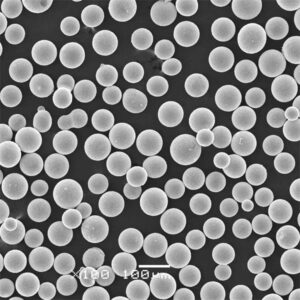
Titanium powder is composed of fine titanium particles used to manufacture parts, coatings, and additives. Key properties include:
- 高い強度対重量比
- 耐食性
- 生体適合性
- 高融点
- 低密度
- Strength retention at high temperatures
Titanium powder is available in various purity grades, particle sizes, and morphologies to suit different production processes and end-use requirements.
The most common production methods for titanium powder are gas atomization and plasma spheroidization. Suppliers offer both crude titanium powders as well as spheroidized, alloyed and plasma purified grades.
Titanium Powder Types
| タイプ | 説明 | アプリケーション |
|---|---|---|
| 純チタン | 99.5-99.9% titanium content | Aerospace, medical, consumer products |
| Ti-6Al-4V | Titanium + 6% aluminum + 4% vanadium | Aerospace, automotive, implants |
| Ti64 | An alternative designation for Ti-6Al-4V | Aerospace, automotive, implants |
| Ti-6Al-7Nb | Titanium + 6% aluminum + 7% niobium | 航空宇宙、医療 |
| Other Titanium Alloys | Various compositions possible | Specialty applications |
Titanium Powder Characteristics
| 特徴 | 詳細 | 意義 |
|---|---|---|
| 粒子径 | Range from 10-250 microns | Determines suitability for additive manufacturing or pressing applications |
| 形態学 | May be irregular, angular, or spheroidal | Spheroidal powders have better flowability |
| 純度 | Grades from CP1 to CP4 based on oxygen, nitrogen, carbon levels | Higher purity grades required for more demanding applications |
| 合金組成 | Varies based on aluminum, vanadium, other alloying content | Alloying elements enhance strength and modify properties |
| 製造方法 | Gas atomized, plasma purified, hydride-dehydride | Affects particle characteristics like size distribution, shape, purity |
チタンパウダー仕様
| パラメータ | レンジ |
|---|---|
| 粒子径 | 10-150 microns typical |
| 酸素含有量 | <0.20% for Grade 1 titanium |
| 窒素含有量 | <0.03% for Grade 1 titanium |
| 炭素含有量 | <0.08% for Grade 1 titanium |
| タップ密度 | 2.2-3.8 g/cc |
| 見かけ密度 | >92% of absolute density |

の応用 チタンパウダー
The unique properties of titanium make its powder suitable for diverse applications across industries:
航空宇宙
- Structural components
- エンジン部品
- Airframes
- Spacecraft
医療・歯科
- Joint replacements
- 歯科インプラント
- 手術器具
- 医療機器
自動車
- Valve systems
- Connecting rods
- Racing components
化学処理
- Corrosion resistant vessels
- 熱交換器
- Pipework
消費者製品
- スポーツ用品
- 時計
- Eyeglasses
アディティブ・マニュファクチャリング
- 航空宇宙部品
- 自動車部品
- 医療機器
- 消費者製品
粉末冶金
- P/M titanium parts
- Master alloys
- Hard metals industry
Global Titanium Powder Suppliers
The complex production methods for titanium powder mean that manufacturing capacity is concentrated in the hands of a few large suppliers with proprietary technologies.
The leading global titanium powder suppliers include:
エーピーアンドシー
Founded: 1997
Headquarters: Montreal, Canada
- Powders: Titanium, titanium alloys, nickel superalloys
- Grades: Ti-6Al-4V, Ti-6Al-7Nb, pure titanium
- Production capacity: 4,000 metric tons annually
- Markets served: Aerospace, medical, energy, automotive
ATI粉末冶金
Founded: 1908
Headquarters: Pittsburgh, USA
- Powders: Titanium, nickel, specialty alloys
- Grades: Ti-6Al-4V Grade 5 and 23
- Production capacity: Over 5,000 metric tons annually
- Markets served: Aerospace, medical, automotive, oil & gas
CRS Holdings
Founded: 1987 Headquarters: Huntersville, USA
- Powders: Titanium, titanium alloys, nickel alloys
- Grades: Ti-6Al-4V, Ti-6Al-7Nb, commercially pure titanium
- Production capacity: 2,000 metric tons annually
- Markets served: Aerospace, defense, medical, automotive
GKNホエガネス
Founded: 1983
Headquarters: Cinnaminson, USA
- Powders: Titanium, steels, nickel alloys
- Grades: Ti-6Al-4V, plasma refined titanium
- Production capacity: Wide range of water and gas atomized powders
- Markets served: Additive manufacturing across industries
大阪チタニウムテクノロジーズ
Founded: 1946
Headquarters: Amagasaki, Japan
- Powders: Titanium alloys, nickel alloys, specialty metals
- Grades: Ti-6Al-4V, Ti-6Al-7Nb, high purity titanium
- Production capacity: Leading supplier in Japan
- Markets served: Aerospace, automotive, medical, electronics
ピュリス
Founded: 2019 as joint venture by Titanium Industries (1935) and Mitsui (1947)
Headquarters: Jerusalem, Israel
- Powders: Titanium alloys
- Grades: Ti-6Al-4V Grade 5
- Production capacity: Around 2,000 metric tons annually
- Markets served: Aerospace, medical, defense, automotive
Reading Alloys
Founded: 1988
Headquarters: Robesonia, USA
- Powders: Master alloys, titanium alloys
- Grades: Custom titanium master alloys
- Production capacity: Range of atomization equipment for different metals
- Markets served: Supplier to powder metal producers
SLMソリューション
Founded: 1996
Headquarters: Lubeck, Germany
- Powders: Titanium alloys, aluminum alloys, nickel alloys, tool steel
- Grades: Ti-6Al-4V Grade 5 and 23, aluminum alloys
- Production capacity: Key supplier for additive manufacturing industry
- Markets served: Aerospace, medical, automotive sectors
Titanium Powder Pricing
| サプライヤー | グレード | 粒子径 | 価格 |
|---|---|---|---|
| エーピーアンドシー | Ti-6Al-4V | 45-100ミクロン | $55/kg |
| ATI粉末冶金 | Ti-6Al-4V ELI | 63-106 microns | $50/kg |
| CRS Holdings | Ti-6Al-4V | 75~150ミクロン | $45-50/kg |
| GKNホエガネス | Ti-6Al-4V plasma | 15-45ミクロン | $120+/kg |
| Osaka Titanium | Pure titanium | 45 microns | $100/kg |
Titanium powder is more expensive compared to steel powder costs due to complex manufacturing and economies of scale. However, buyers focus on quality, purity and product performance instead for critical applications.
Titanium vs Alternative Powders
Titanium vs. Steel
Titanium has 40% lower density than steel and retains strength better at elevated temperatures. It has excellent corrosion resistance due to surface oxide layer. More expensive than stainless steel powder.
Titanium vs. Aluminum
Almost twice as strong as aluminum powder but with only 60% higher density. Maintains properties at higher temperatures. Much better corrosion resistance than aluminum due to oxide layer.
Titanium vs. Nickel Superalloys
Titanium has lower density providing higher specific strength. Nickel alloys can operate at extreme temperatures exceeding titanium’s useful limits. Titanium cheaper alternative to expensive superalloys.
Titanium vs. Cobalt Chrome
Half the density of cobalt chrome alloys. Excellent biocompatibility unlike concerns with cobalt and chromium release in body. Significantly cheaper material option.
Choosing a チタンパウダー サプライヤー
Key factors in choosing a titanium powder supplier:
技術力
- Ability to manufacture grades needed
- Quality control over entire production process
- 化学組成の一貫性
Track Record
- Years of experience in industry
- 製品の品質とサービスに対する評判
品質認証
- AS9100, ISO 9001
- Specific aerospace, defense or nuclear certifications
カスタマイズ
- Ability to customize alloy composition and particle characteristics
価格
- Quantity discounts may be available
- Large buyers can negotiate pricing
- Pay premiums for high purity grade powder
リードタイムズ
- Typical 6-8 weeks for ordered powders
- Rush orders possible for additional fee
所在地
- Shipping costs a significant part of powder price
- Onsite visits useful to audit supplier
よくあるご質問
Q: What is the difference between commercially pure titanium vs titanium alloy powder?
A: Commercially pure titanium powder has 99.5-99.9% titanium content with low oxygen, nitrogen and carbon. Titanium alloy powders like Ti-6Al-4V contain aluminum, vanadium, or other elements to enhance properties like strength.
Q: What particle size titanium powder is optimal?
A: For pressing and sintering 75-150 microns is common. For additive manufacturing processes, finer 15-45 micron powder is preferred to achieve good resolution.
Q: Does titanium powder require special handling precautions?
A: Yes, titanium fines are flammable and create explosion hazard. Inert gas blanketing and proper grounding is used. Water contact causes hydrogen absorption issues.
Q: How to determine which titanium grade is best for my application?
A: Consult closely with potential suppliers on technical requirements. Ti-6Al-4V is the most common grade but others like Ti-6Al-7Nb suit specific needs. Get test samples to evaluate performance.
Q: What methods can produce titanium powder suitable for 3D printing?
A: Gas atomization and plasma spheroidization create fine spherical titanium powders optimal for additive manufacturing. Hydride-dehydride and mechanical milling methods also produce printable powder.
Q: What post-processing is required on additively manufactured titanium parts?
A: Hot isostatic pressing (HIP) helps eliminate porosity in printed parts. Additional heat treatments, surface finishing, and machining may be needed depending on final properties and tolerances required.